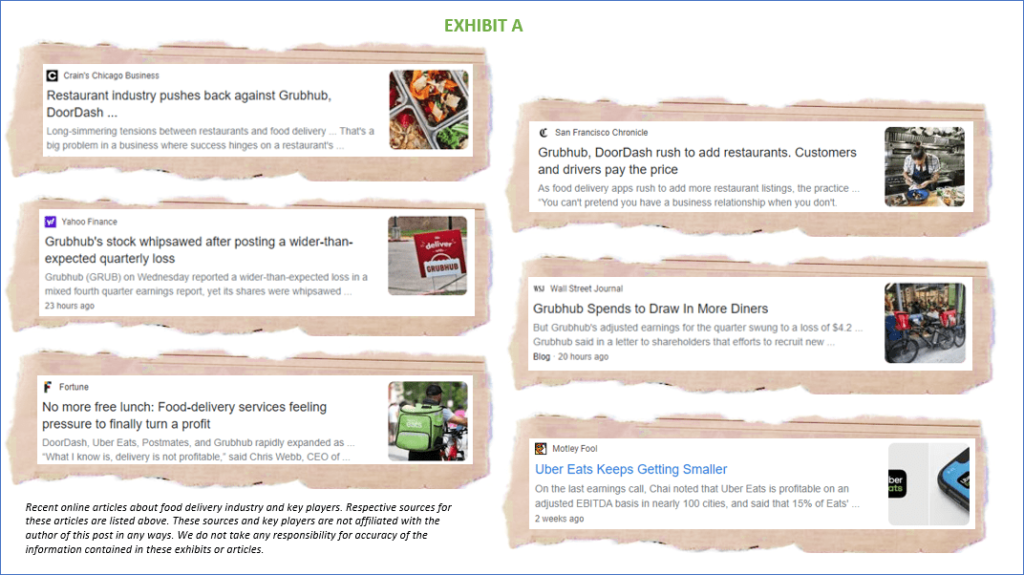
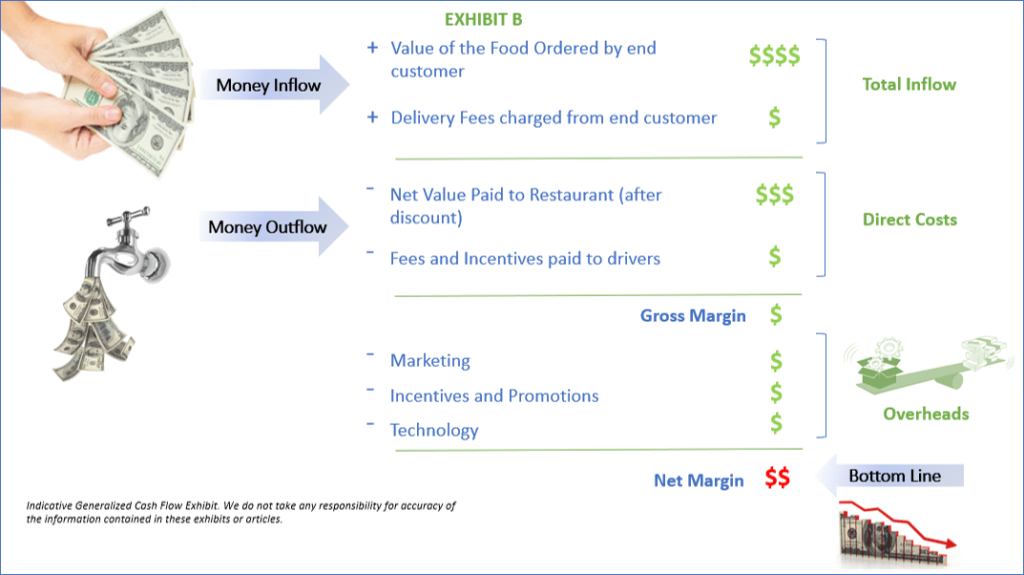
Restaurants that have survived the pandemic are now threatened by recent inflation. People are quickly feeling the price increases among everyday items affect their decisions.
Now restaurant owners are faced with the effect inflation has on the industry. Inflation can cause an increase in costs in all aspects of the restaurant industry. That includes rent, food, labor, utilities, and insurance.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, wholesale food costs were 17% higher in March than last year. Along with a rise in hourly earnings for employees than the prior year.
Establishments deal with rising costs of goods while seeing fewer customers walk through the door. Some people are eating out less and finding it more affordable to cook at home. Cutting back is the first thing people begin to do when prices rise. Diners are more hesitant to dine out because their everyday expenses rapidly increase. With interest rates rising, people find it more challenging to borrow money or lines of credit as well.
Here are 5 tips to help you fight inflation, save money and keep customers in the door.
1. Find Ingredient substitutions
Restaurant owners can agree that food costs are one of the biggest challenges, especially when it comes to inflation. Taking a closer look at your inventory costs can be beneficial by revisiting your cost analysis. Is there any ingredient that you use a lot of that’s seriously cutting into your budget? Or maybe a hot-selling dish brings significant revenue but includes pricey ingredients which impact your profit.
By exploring ways you can swap ingredients for something less pricey, you will begin to see savings.
2. Audit your menu

To do a proper menu audit, take all the factors into account in your menu and the profits you make on each dish. Sort the menu items out from the most highly profitable to the least. When you’re finished, evaluate what you can cut off your menu and save for something more critical, or put the money elsewhere into another dish.
To do this properly, you’ll have to take a good look at your menu and know the profit you make on each dish. Segment your items into four groups and make adjustments based on their performance. Take into account which dishes really work and which one’s dont.
3. Consider Price Changes
Increasing your prices may actually prove to be more beneficial to your establishment. Consider adding ingredients to make the cost more valuable, or try including a premium side to bundle and spend more.
4. Reduce food waste

If you’re not on top of monitoring your inventory, you may risk a big part of your budget by not accounting for food costs. Don’t just count inventory; dig into your numbers and understand where exactly you are losing money due to waste and over portion sizes. If you notice that guests are finishing their plates, you may need to look into smaller portion sizes. Optimize your recipes and use the most out of all your ingredients.
5. Try to Reduce Food Costs
Profitable restaurants usually incur 27%-36% of their revenue on direct food costs. In the current inflationary environment, keeping a close track of our direct food costs is more important than before. Accurate and consistent ordering from reliable vendors should also help. Do not hesitate to ask for price break volumes and freeze food if it makes sense. We occasionally see local merchants and wholesale clubs like Restaurant Depot, Costco and Sam’s Club offering limited-time deals on quality food products. A lot of small independent restaurants we have talked to do not hesitate to buy through such retailers, especially the products which they have tried before.
ABOUT CHOWEASY
ChowEasy is a free app that helps restaurants attract new, quality customers from their local area. Restaurants attract passionate foodies with easy-to-setup promos. No upfront costs or commitments!